This age group includes booster data and charts. Here we do see a continuing benefit of vaccination against hospitalization.
 Dave’s notes:
Dave’s notes:
- In the following charts we can conclude, for the 18-49 year old age group, that being vaccinated and boosted appears to offer protection for being hospitalized with Covid in the most recent weeks’ data available, but the boosted actually have higher rates of testing positive than the vaccinated or unvaccinated. There are too few deaths in this age group to draw any conclusions.
- There are 9 charts in this set, 3 charts each for cases, hospital admissions, and deaths. Each set of 3 charts consists of the actual events per week (cases, admissions, or deaths); the rate per 100k each week, and the proportion of events compared to the proportion of the vaccinated population.
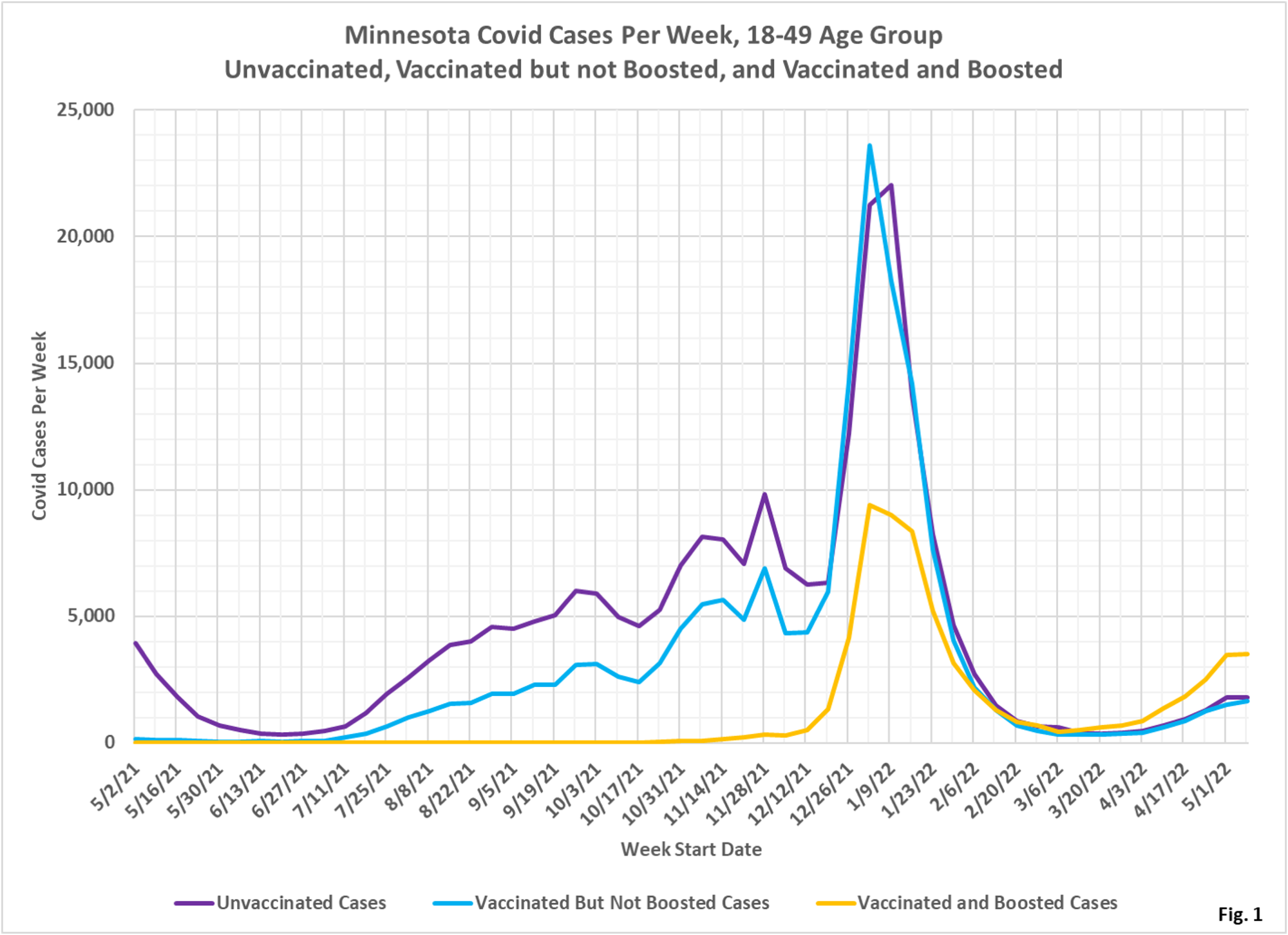
- Fig. 1: This chart plots the cases in the 18-49 age group per week among the unvaccinated, vaccinated but not boosted, and vaccinated and boosted populations each week. Since the week of 3/13/2022 there have been more cases each week among the boosted, rather than among the vaccinated but not boosted, or unvaccinated. The boosted are just barely the largest subgroup, but only make up 36% of the population, as will be seen in Fig. 3, for the week of 5/08/2022.
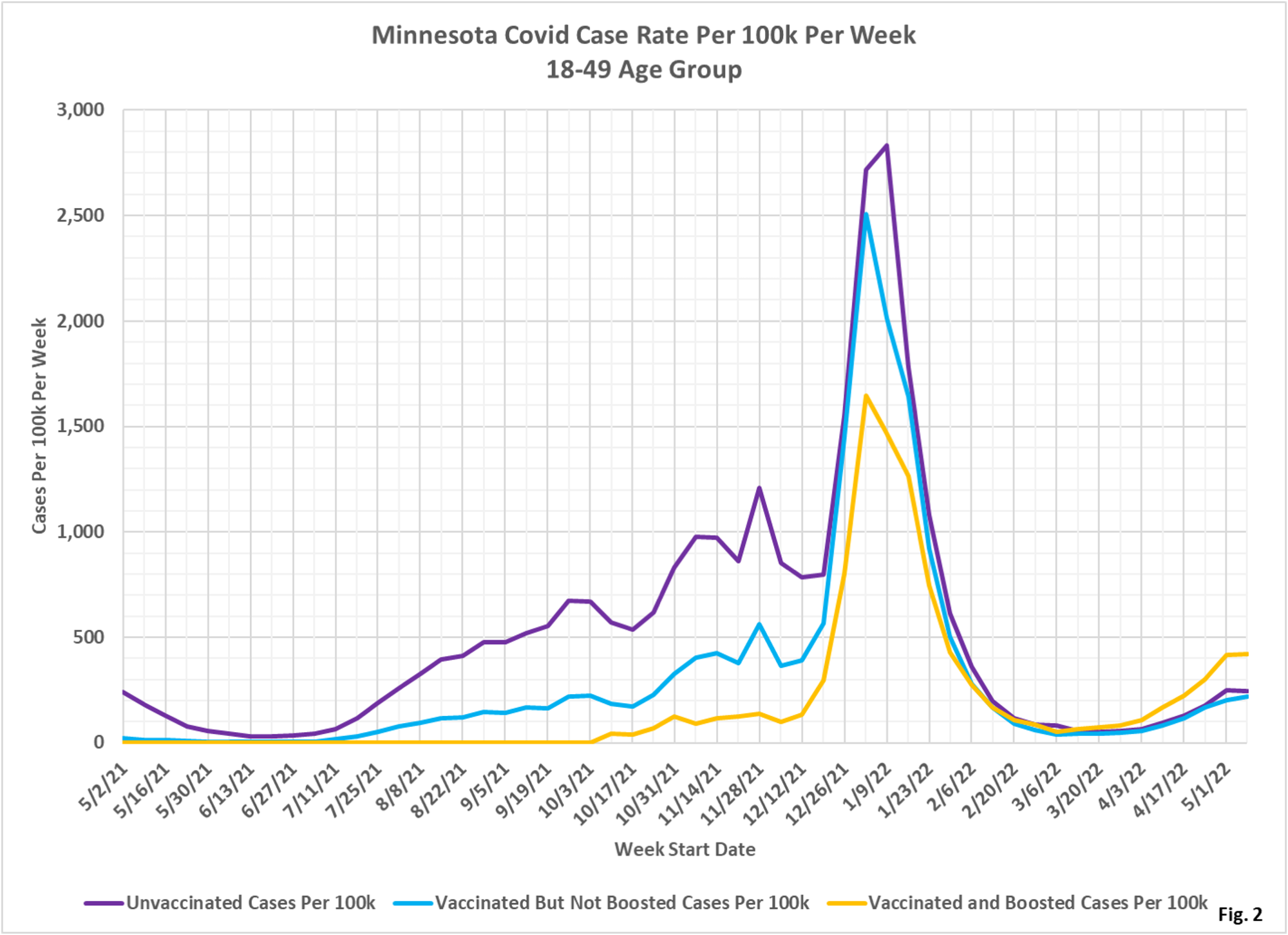
- Fig. 2: This chart displays the case rates per 100k for each subgroup in the 18 to 49 age group. It is interesting the most recent months of data that the boosted have the highest rate of cases per 100k, and the vaccinated but not boosted have the lowest rate of cases per 100k. Earlier in the pandemic being vaccinated or boosted did lower the case rate compared to the unvaccinated.
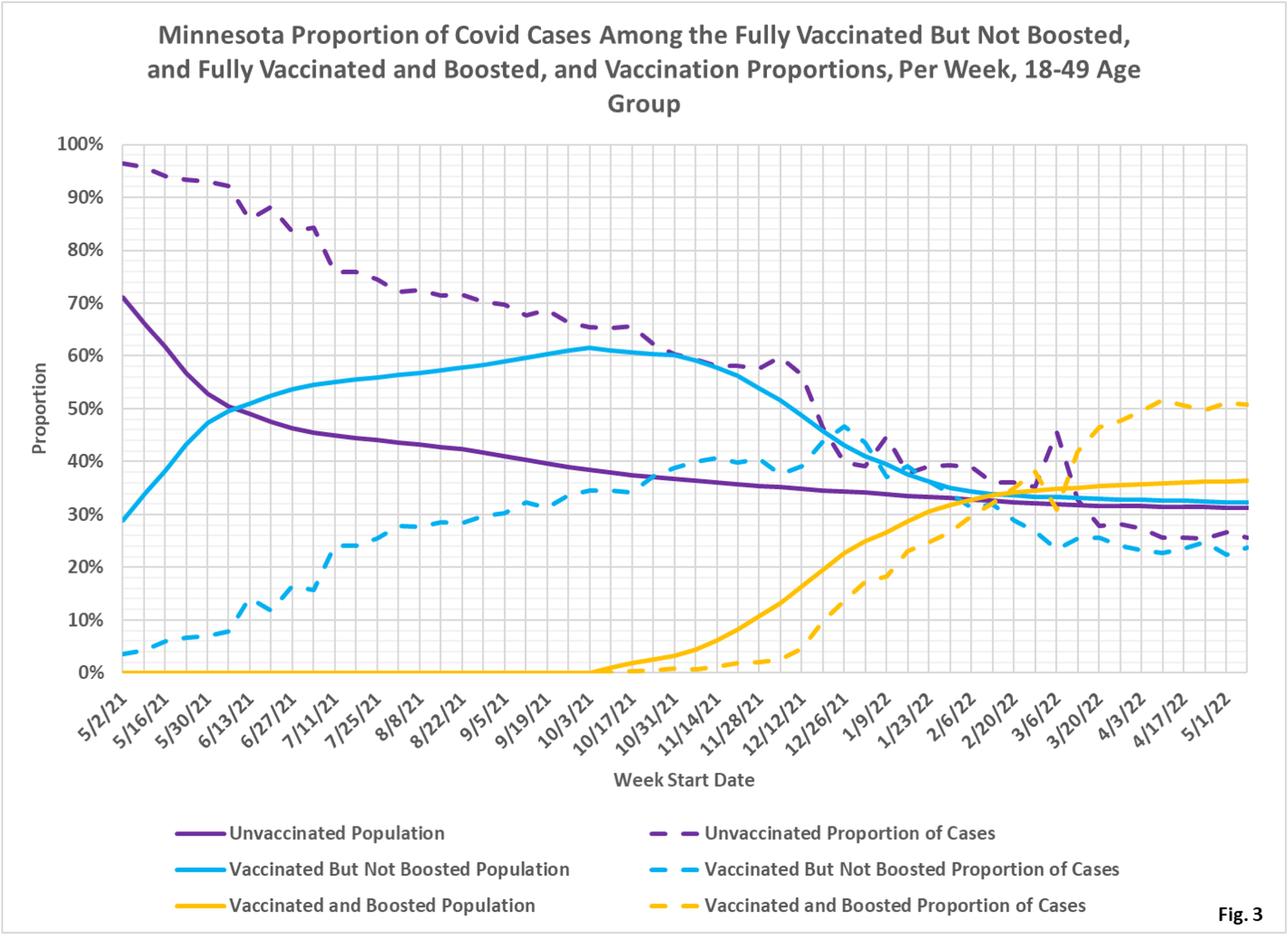
- Fig. 3: This chart displays the proportion of the 18-49 population who are unvaccinated (solid purple), vaccinated but not boosted (solid blue), and vaccinated and boosted (solid gold). For each population group we also display the proportion of cases each week (dashed lines of same color). Note that as people are boosted they are moved from the vaccinated subgroup to the boosted subgroup. The way to interpret this chart is to compare the proportion of breakthroughs to the proportion of vaccinations for each group. Whenever the dashed breakthrough proportion line is below the solid vaccination line of the same color, then that category is underrepresented for population, and that vaccination status might be said to be beneficial (ignoring for now other confounding factors). For the week of 5/8/2022, for example, 36% of this age group was vaccinated and boosted (solid gold line) while this group accounted for 51% of the cases (dashed gold line). We would interpret this to show that being boosted did not reduce an individual’s chances of testing positive for Covid for that week. On the other hand, we can see that being vaccinated but not boosted was very beneficial the week of 5/2/2021 for example (29% vaccinated, but only 4% of the cases) but over time the vaccinated but not boosted subgroup gradually lost the benefit of vaccination, and by the week of 5/2/2022 the vaccinated were 32% of the age group and accounted for 25% of the cases, showing modest benefit for being vaccinated.
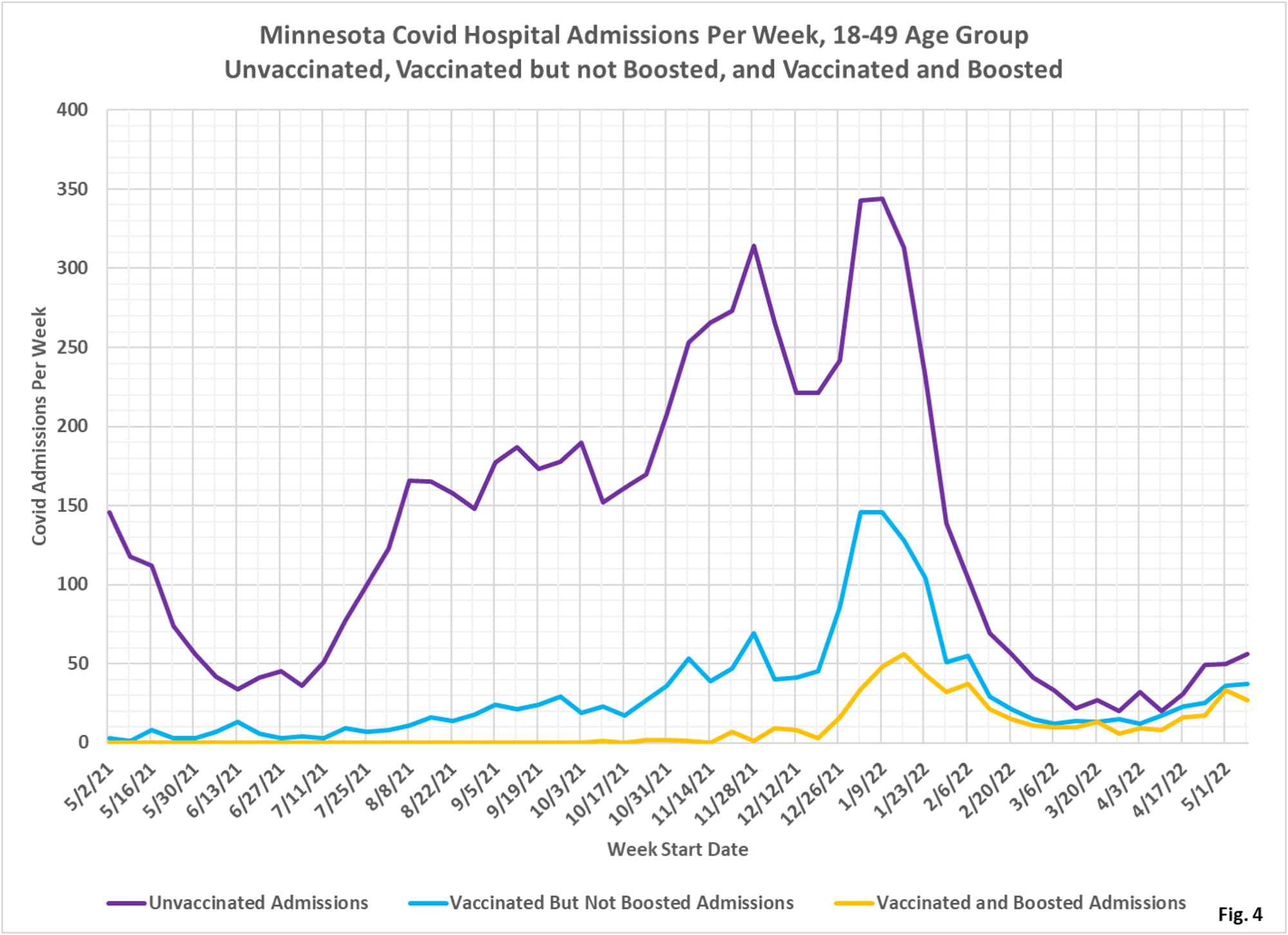
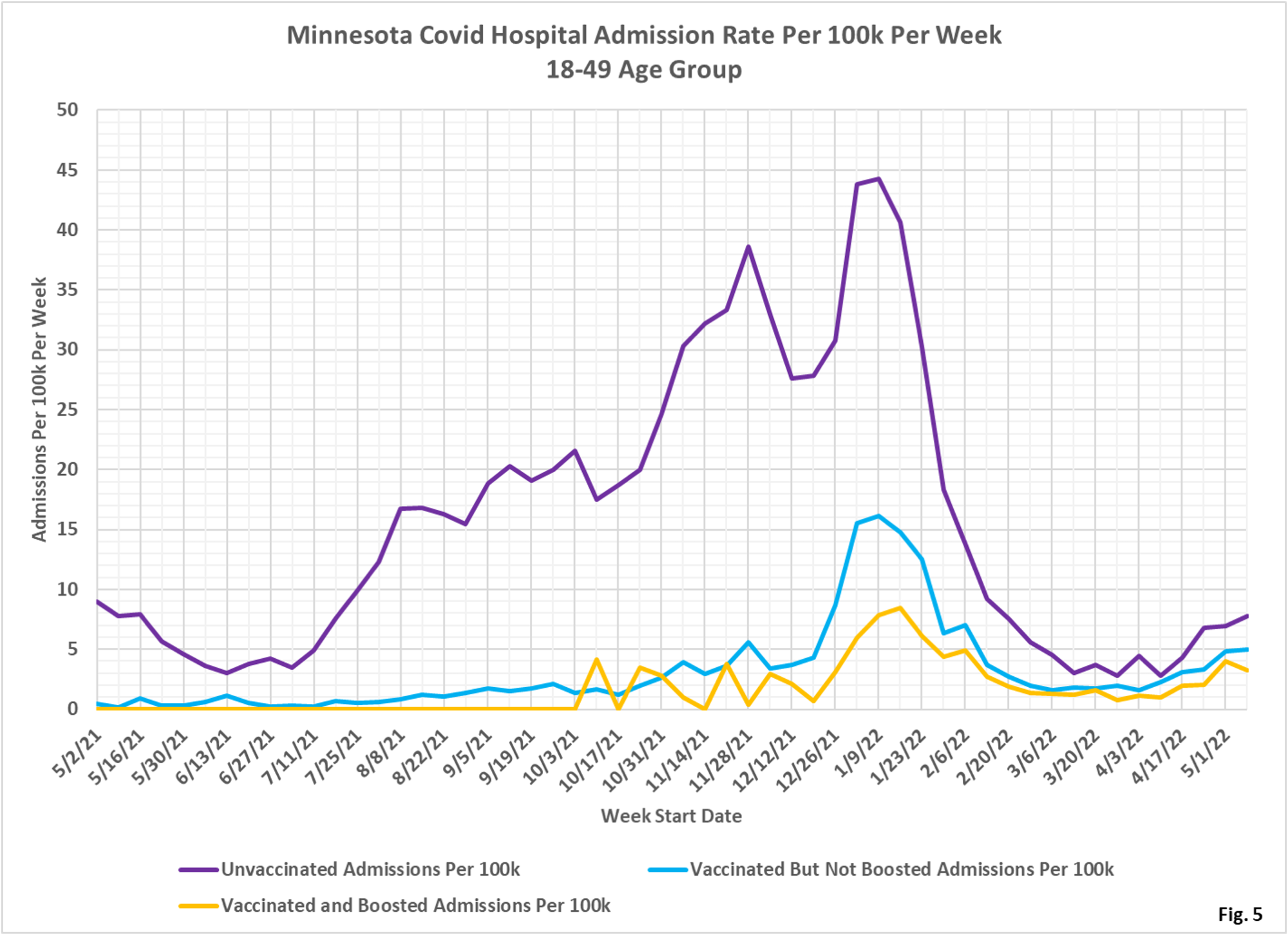
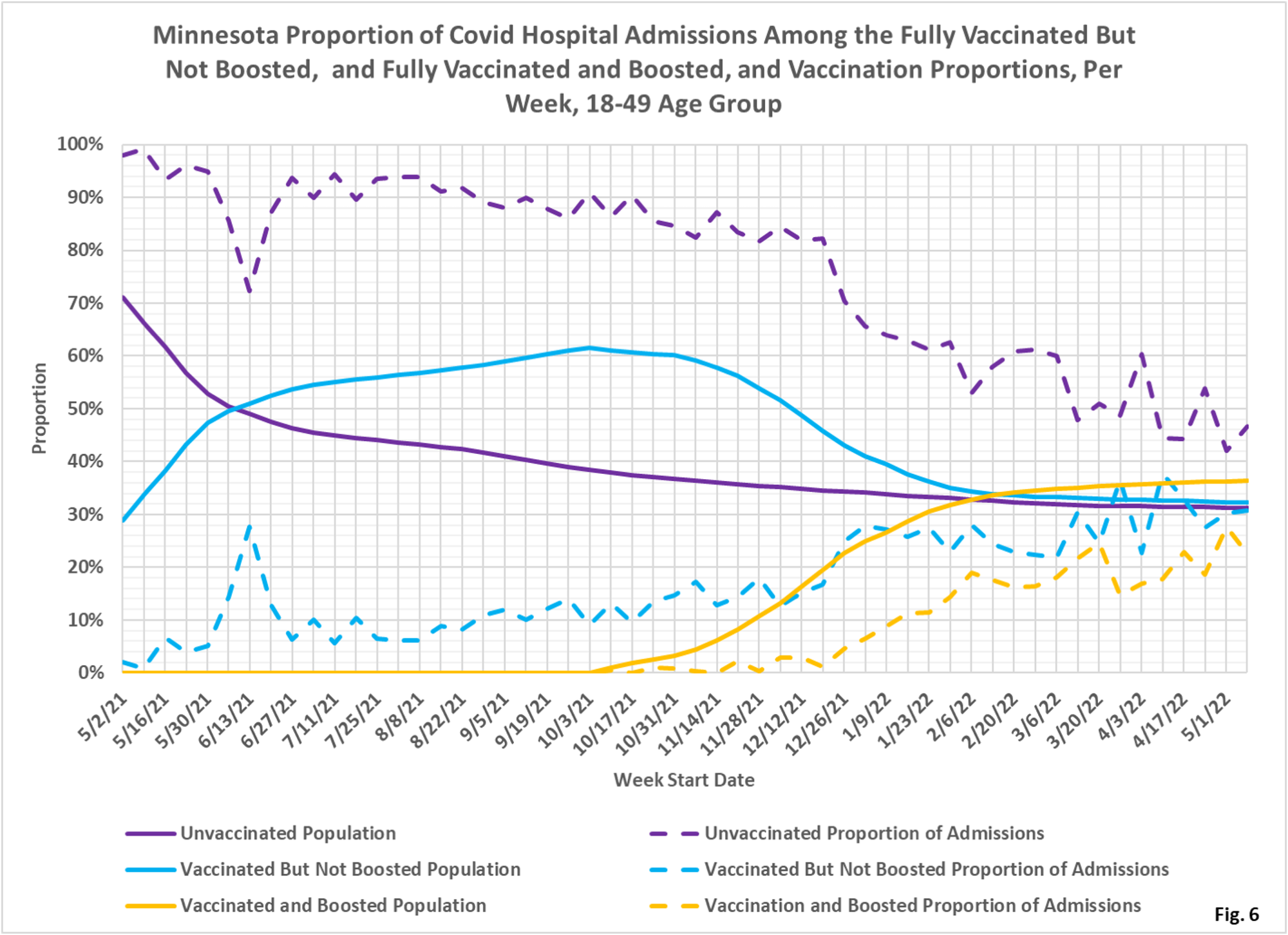
- Fig. 4-6: These charts display the hospital admissions, hospital admission rates per 100k, and hospital admissions proportions for the 18-49 age group, in an identical format to the case charts in Fig. 1 through Fig. 3. The boosted have made up the lowest number of admissions in recent months (Fig. 4). The admissions per 100k for the unvaccinated are highest, with the vaccinated being second highest, and the boosted having the lowest rates of admissions in recent months (Fig. 5). Fig. 6 shows that admissions among the unvaccinated have been disproportionately high throughout the pandemic. Admissions among the boosted remain disproportionately low compared to the boosted proportion of the population that is boosted.
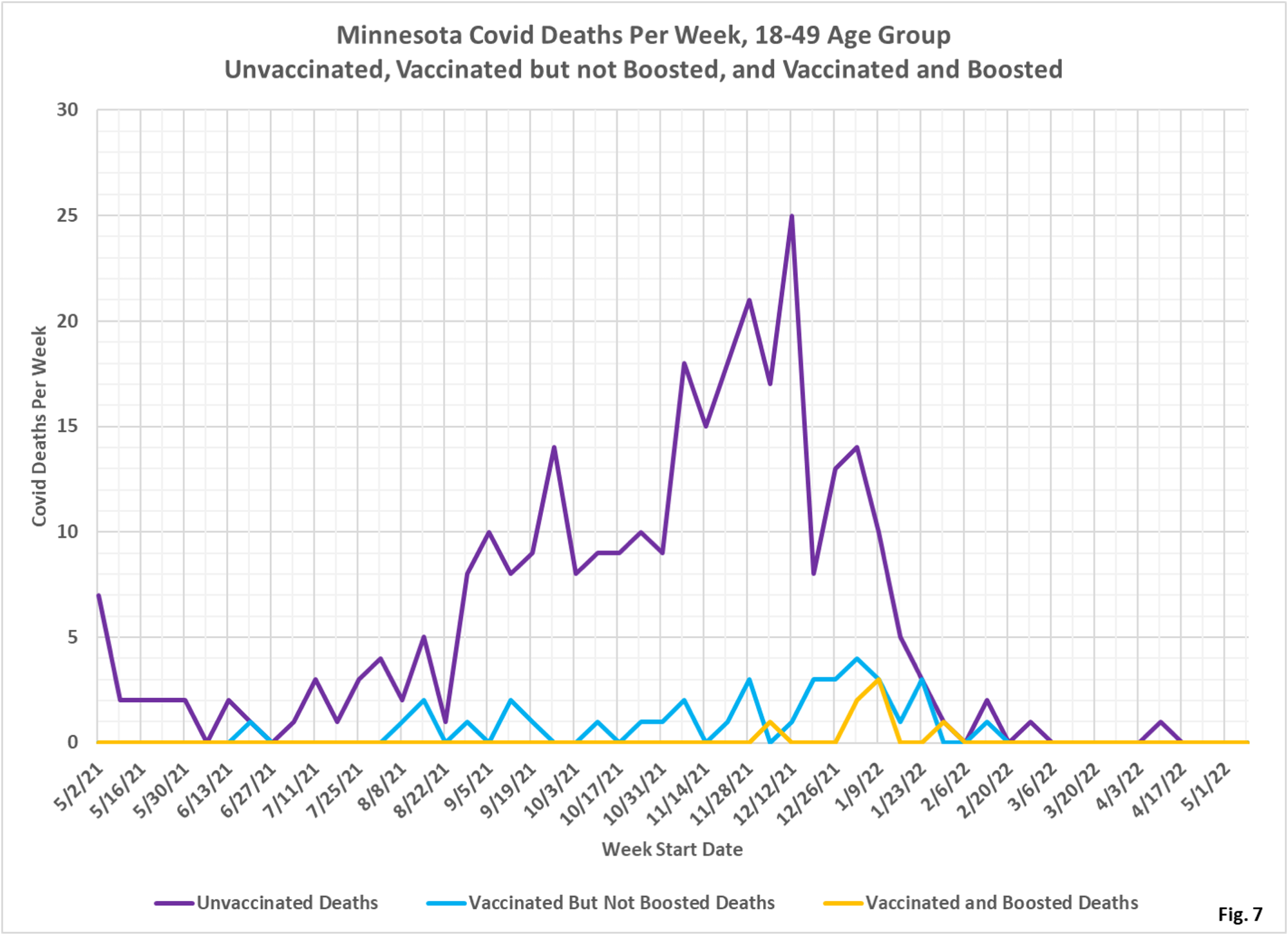
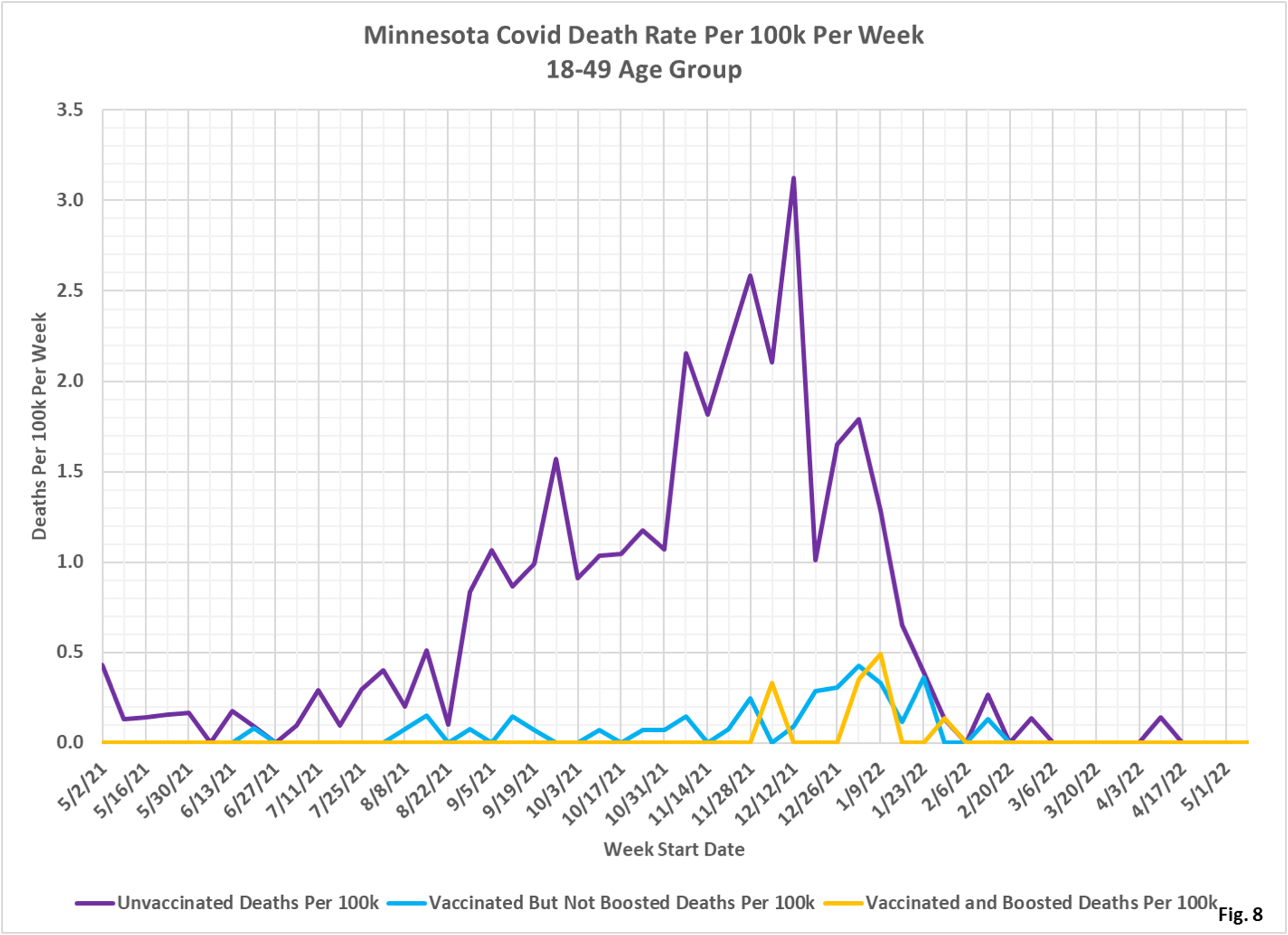
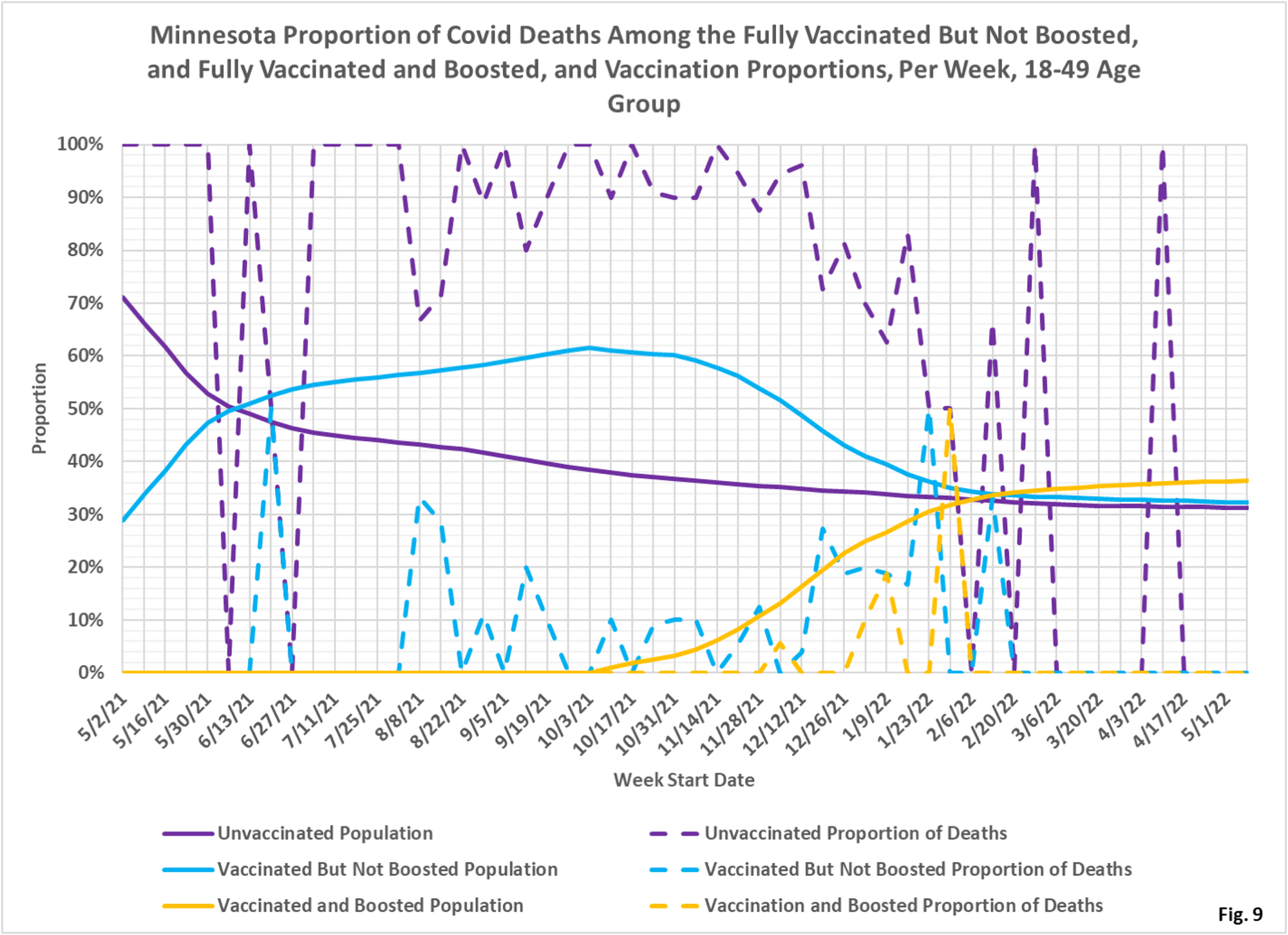
- Fig. 7-9: These charts display the deaths, deaths rates per 100k, and deaths proportions for the 18-49 age group, in an identical format to the case charts in Fig. 1 through Fig. 3. The unvaccinated had the greatest number of deaths during the Omicron wave in late 2021/early 2022, but in recent weeks there are very few deaths in either of the subgroups (Fig. 7). Fig. 8 shows that the rates of death per 100k for each subgroup is very low in the most recent months of data, matching Fig. 7. Fig. 9 shows that deaths proportions are highly variable, and that the unvaccinated are over-represented throughout the pandemic.
- All data is obtained from the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) Vaccine Breakthrough Weekly Update web site https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/coronavirus/stats/vbt.html. A data file on this site, vbtadultcirates.xlsx, contains all of the age group data.
- MDH defines the fully vaccinated (what we have termed vaccinated but not boosted) as those who have not received a booster after completing their primary vaccination series, and had been vaccinated at least 14 days prior to testing positive.
- MDH defines the boosted as those who have received any additional vaccination shots after completing their primary vaccination series, and also received the booster at least 14 days prior to testing positive. In addition, booster doses were only counted after 8/13/2021, the date the CDC first began recommending booster shots.

